Understanding DOP (Dilution of Precision): Its Function and Operation
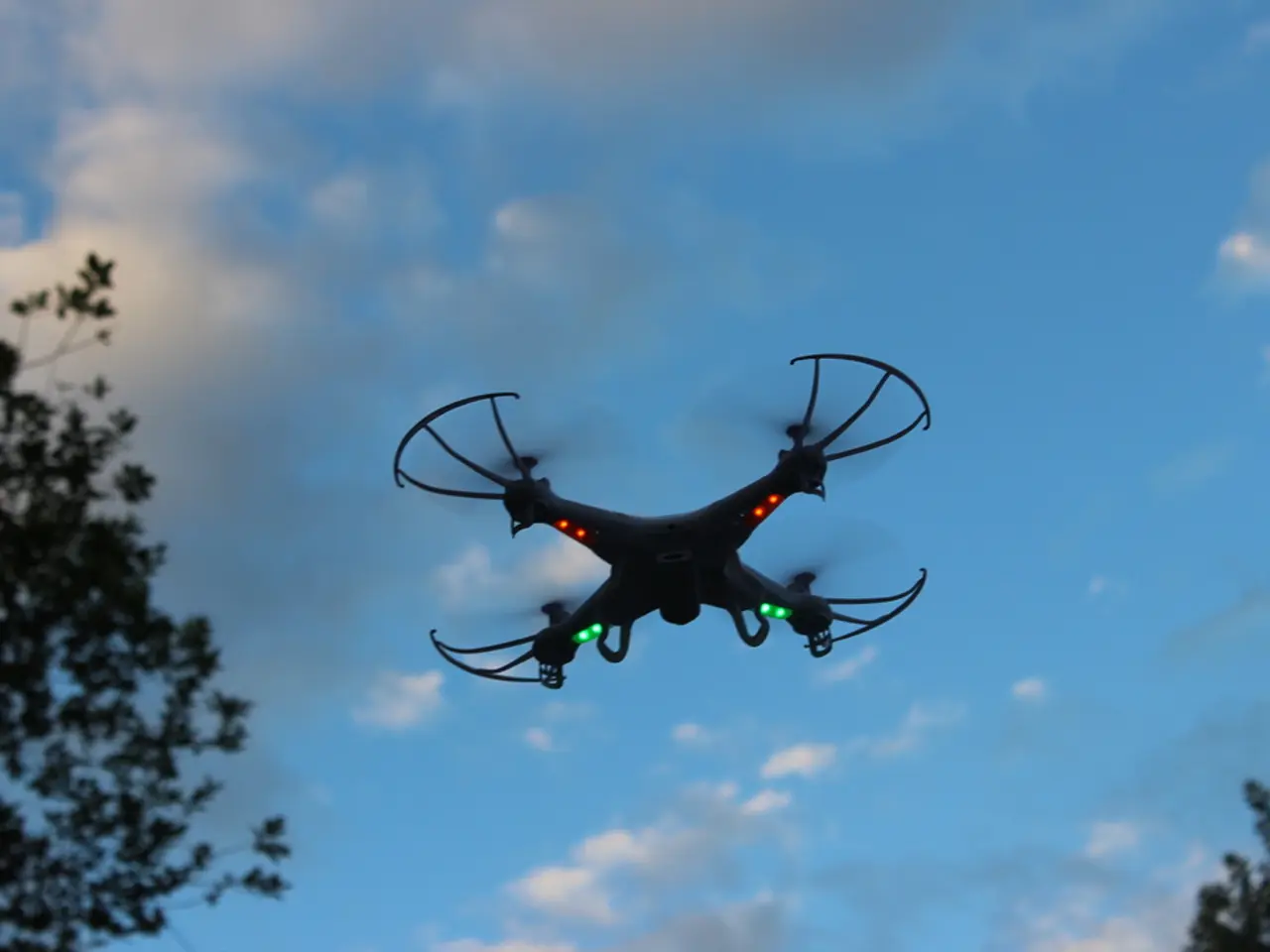
In the realm of modern drone technology, one factor that significantly impacts the precision and accuracy of GPS-guided flights is Dilution of Precision (DOP). This article aims to shed light on this crucial concept and its implications for drone operations.
DOP directly affects GPS/GNSS positioning accuracy in drone operations by quantifying how satellite geometry impacts the reliability of the position fix. Lower DOP values mean better satellite distribution in the sky and thus higher positional accuracy, while higher DOP values indicate poor satellite geometry and increased potential positioning errors.
DOP is divided into several categories relevant for drone navigation:
- HDOP (Horizontal DOP): Accuracy of latitude and longitude.
- VDOP (Vertical DOP): Accuracy of altitude, important for altitude estimation in drones.
- PDOP (Position DOP): Combines horizontal and vertical accuracy, representing overall 3D precision.
- GDOP (Geometric DOP): Includes time accuracy alongside position.
In drone operations such as aerial surveying, photogrammetry, or LiDAR mapping, low DOP ensures more precise georeferencing of collected data and reliable flight path execution. Conversely, high DOP due to satellites clustered in one part of the sky, or obstructions like buildings or trees blocking some satellite signals, results in degraded accuracy, causing errors in mapping outputs or autonomous navigation.
Modern drone flight planning software often uses real-time or forecasted DOP values to select optimal flight times and locations where satellite geometry is best, minimizing the need for costly post-processing corrections and repeat flights.
For drones conducting aerial surveys, photogrammetry, or LiDAR mapping, low Dilution of Precision ensures better georeferencing of collected data. Dilution of Precision quantifies the potential positional error introduced by the spatial configuration of satellites relative to a receiver.
It's essential to note that while DOP reflects satellite geometry, weak signals or interference can affect the ability to receive accurate data, which can compound errors. To reduce DOP during drone operations, planning flights during times of optimal satellite geometry using mission planning apps, or supplementing with RTK/PPK systems, can help improve accuracy.
Dilution of Precision is critical in any operation relying on GPS or GNSS for location accuracy, including drone flight planning, surveying and mapping, autonomous vehicle navigation, maritime and aviation positioning, and timing synchronization in telecom and power grids.
As satellites are constantly moving in orbit, Dilution of Precision values change throughout the day. Flight planning tools and GNSS applications often provide Dilution of Precision forecasts to help operators choose optimal times for missions.
In summary:
- Good satellite geometry (low DOP) = better GPS position accuracy for drones
- Poor satellite geometry (high DOP) = reduced positioning accuracy, affecting drone navigation and data quality
This makes monitoring and managing DOP critical for precise and dependable drone missions relying on GNSS positioning.
[1] Source: GPS World [2] Source: DroneDeploy [3] Source: Pix4D
Read also:
- UNEX EV, U Power's collaborator, inks LOI with Didi Mobility for the implementation of UOTTA battery-swapping vehicles in Mexico.
- North America's Smart Meter Market Forecast 2025: Wave Two Rollouts Thrive, Accounting for 75% of Yearly Shipments by 2030 - According to ResearchAndMarkets.com
- Stratospheric Blockchain Network Launched by World Mobile and Protelindo
- China issues new advisory, suggesting businesses to shun Nvidia H20 Chips